
Undergraduate students’ attitudes towards mathematics and computer programming in biology
Gaurav Kandlikar1, Robin Costello2, Quyen Le1, Margaret Adams2, Catherine Clark2, Dee Dolce2, Justin Uralil2
slides: https://talks.gklab.org/esa-2025-qcb/
contact: gkandlikar@lsu.edu
1 Louisiana State Univ. 2 Univ. at Buffalo
What do students make of this integration?
How do they perceive the value of emphasizing the quantitative and computational dimensions of biology (‘QCB’) in coursework?
Who will choose to take biology courses that emphasize QCB, and what will shape students’ success in these courses?
How can we use this information to improve classroom education?
Framework
Adapted from Expectancy Values Theory, Wiggins & Eccles (2000)
Framework
Adapted from Expectancy Values Theory, Wiggins & Eccles (2000)
Goal: Characterize students’ task values towards the incorporation of mathematics and computer programming in biology
Approach
Quantify task values with a validated instrument (MBVI, Andrews et al. 2017)
Explore what gives rise to variation in these task values
Query further perspectives through open-ended questions
Task values
The MBVI asks 11 questions to characterize students’ task values regarding mathematics in biology.1
We summarized each student’s interest, utility, and costs score using confirmatory factor analysis.
Responses from 219 biology students at an R1 University

Task values
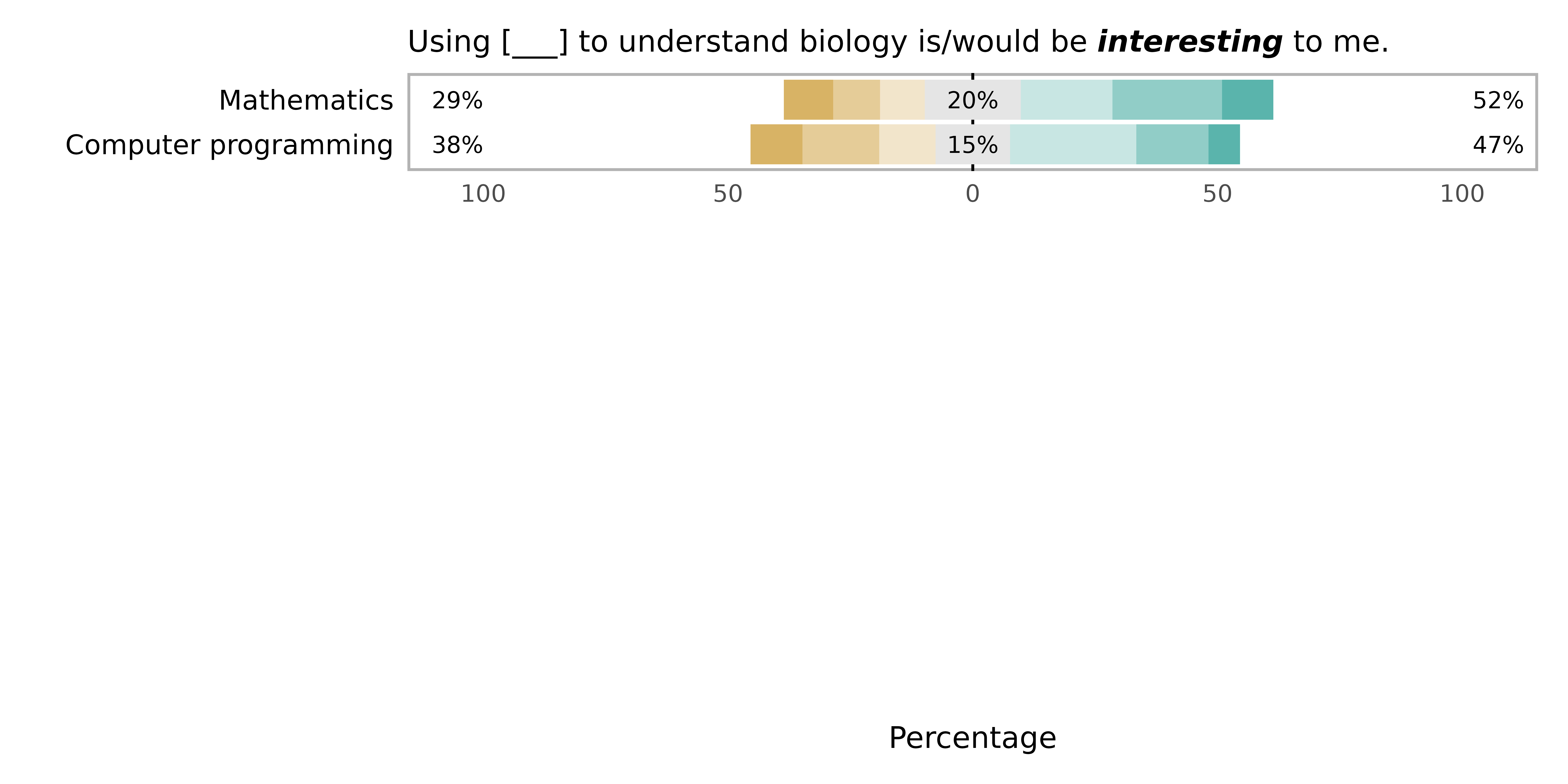
Responses to other questions within each construct follow similar trends (Bayesian CFA); click here for details
Task values
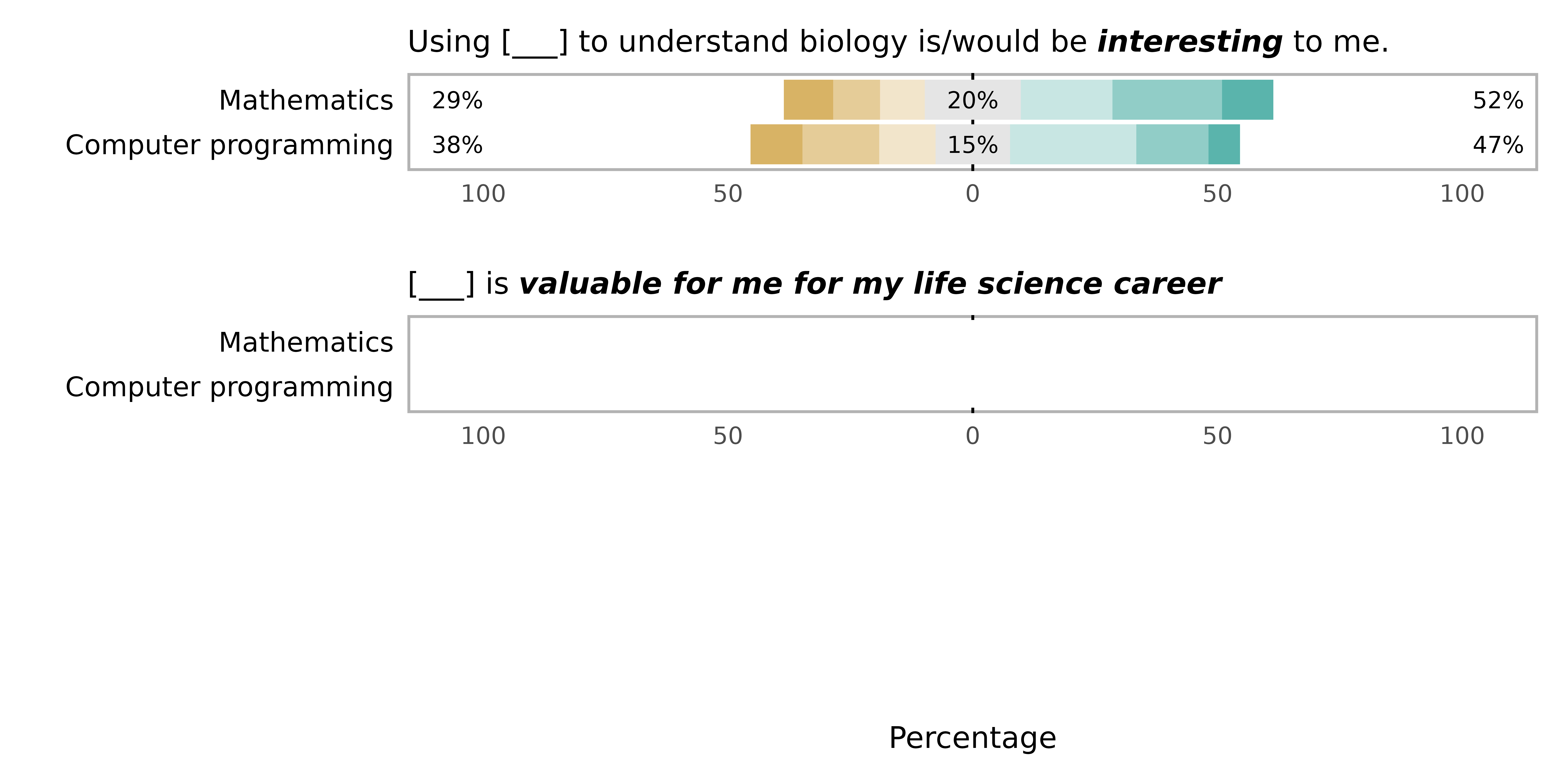
Responses to other questions within each construct follow similar trends (Bayesian CFA); click here for details
Task values
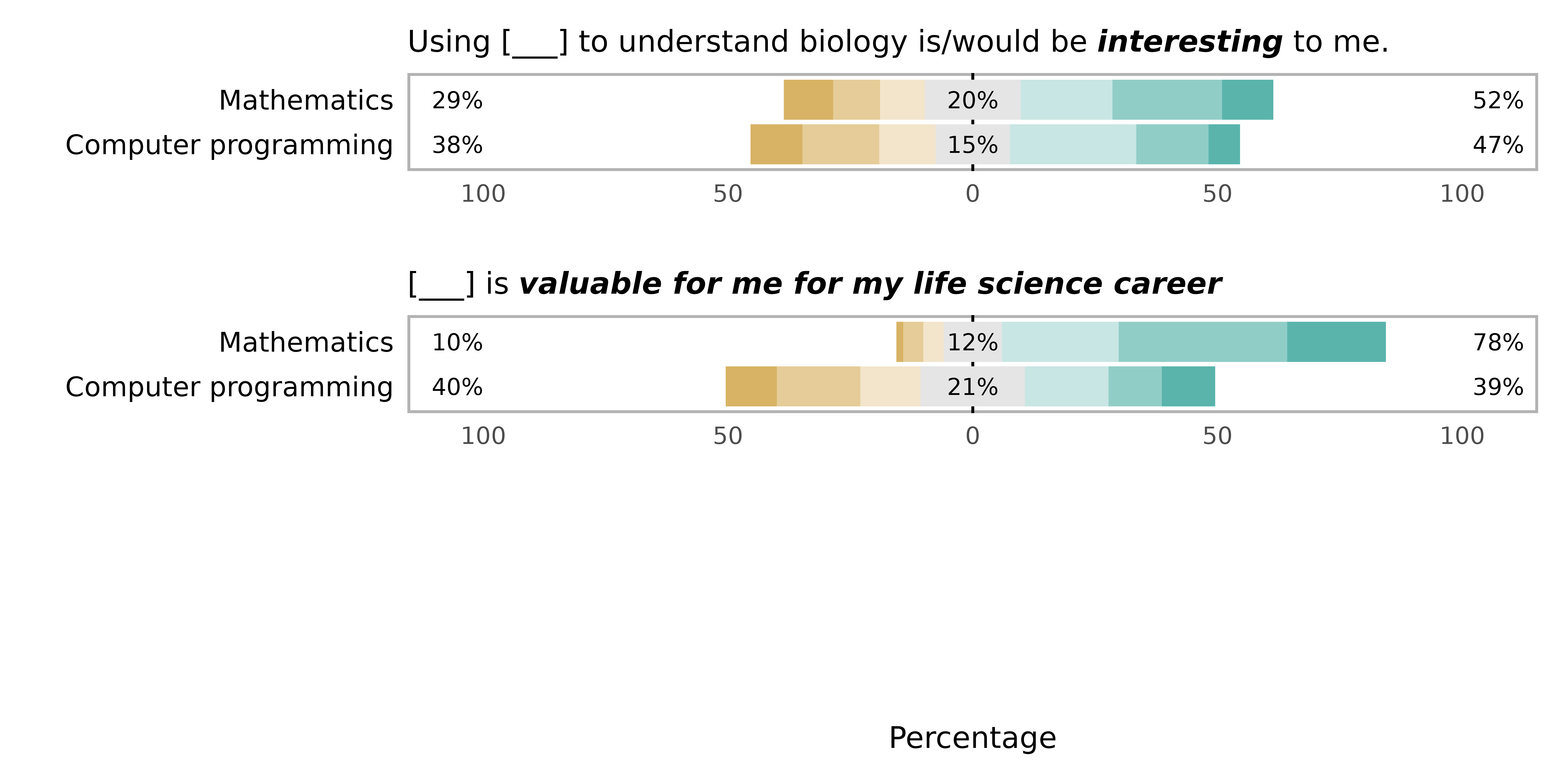
Responses to other questions within each construct follow similar trends (Bayesian CFA); click here for details
Task values
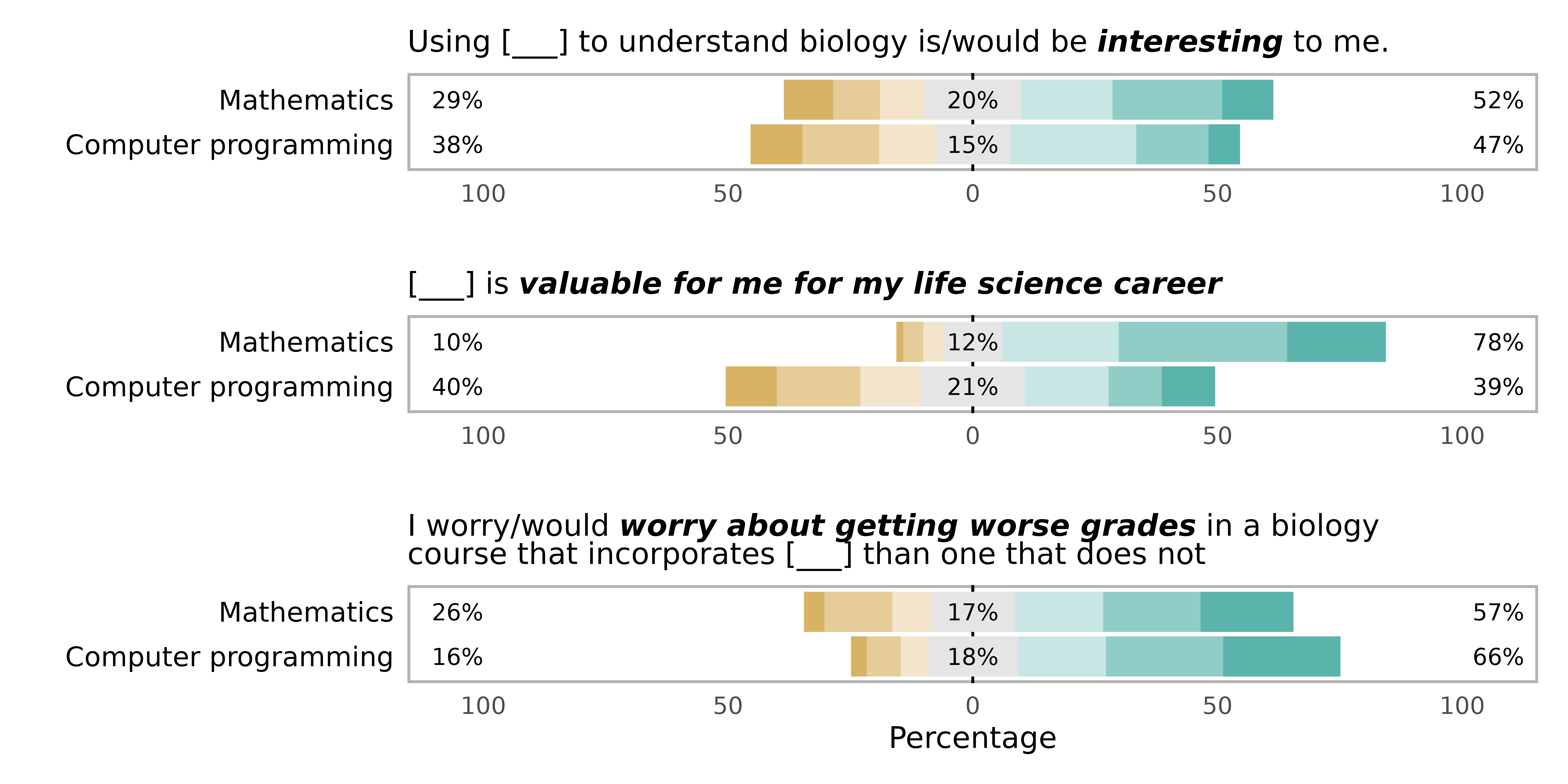
Responses to other questions within each construct follow similar trends (Bayesian CFA); click here for details
What obstacles do students foresee?
- “Are there obstacles that you think you would face in biology courses that incorporate math/computer programming? What obstacles do you think you would face in this type biology course?”
What obstacles do students foresee?
- “Are there obstacles that you think you would face in biology courses that incorporate math/computer programming? What obstacles do you think you would face in this type biology course?”
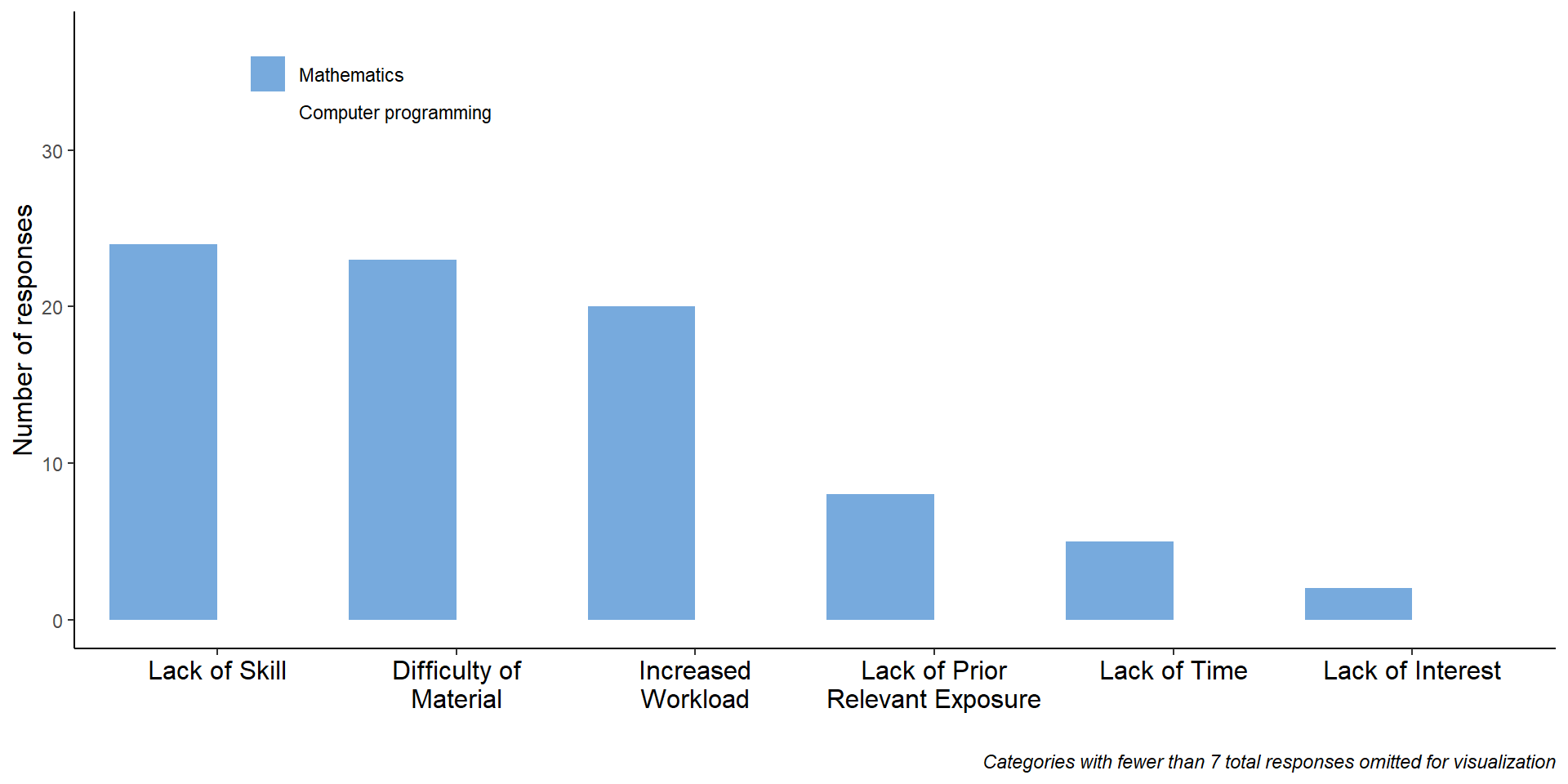
What obstacles do students foresee?
- “Are there obstacles that you think you would face in biology courses that incorporate math/computer programming? What obstacles do you think you would face in this type biology course?”
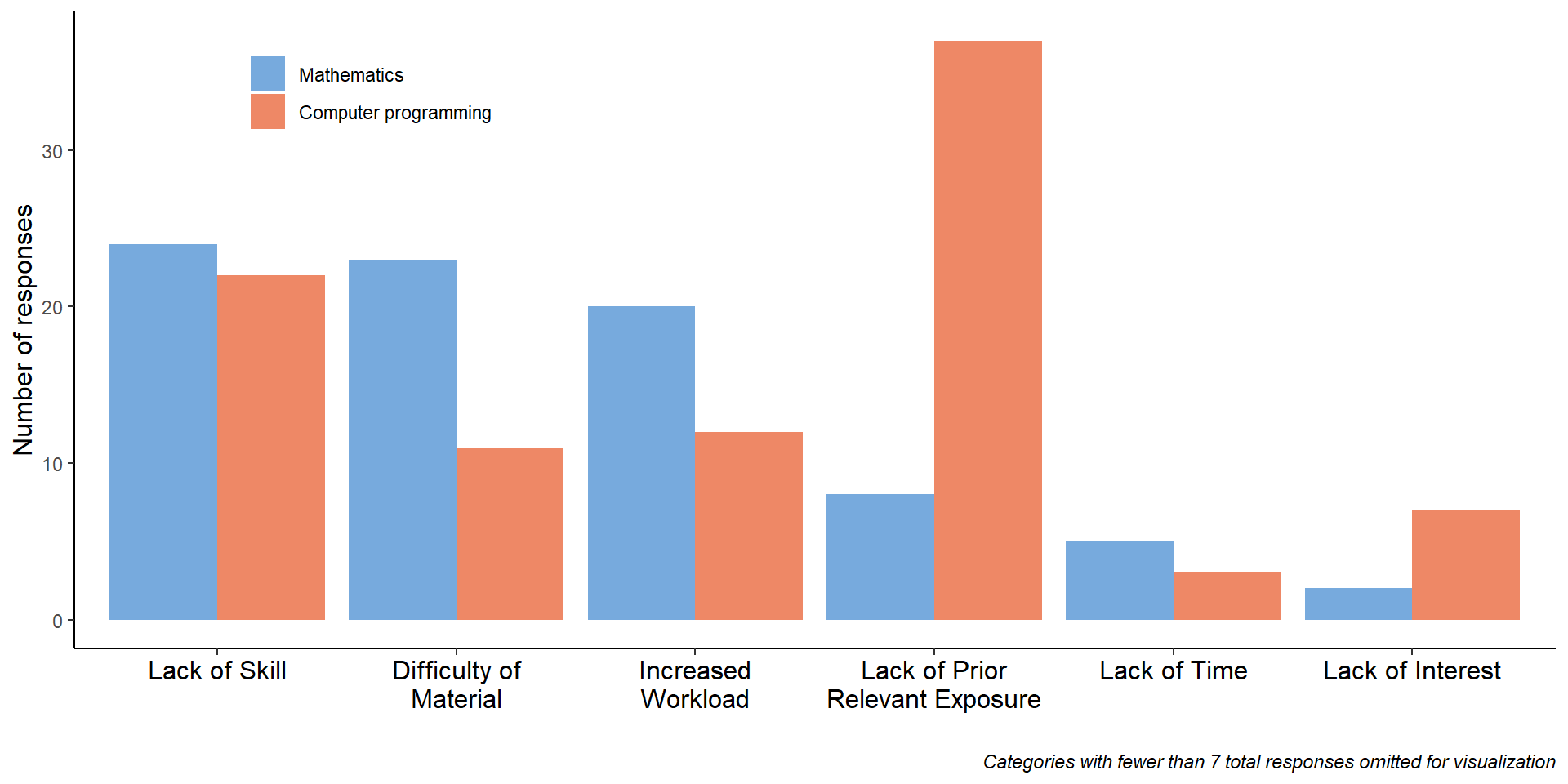
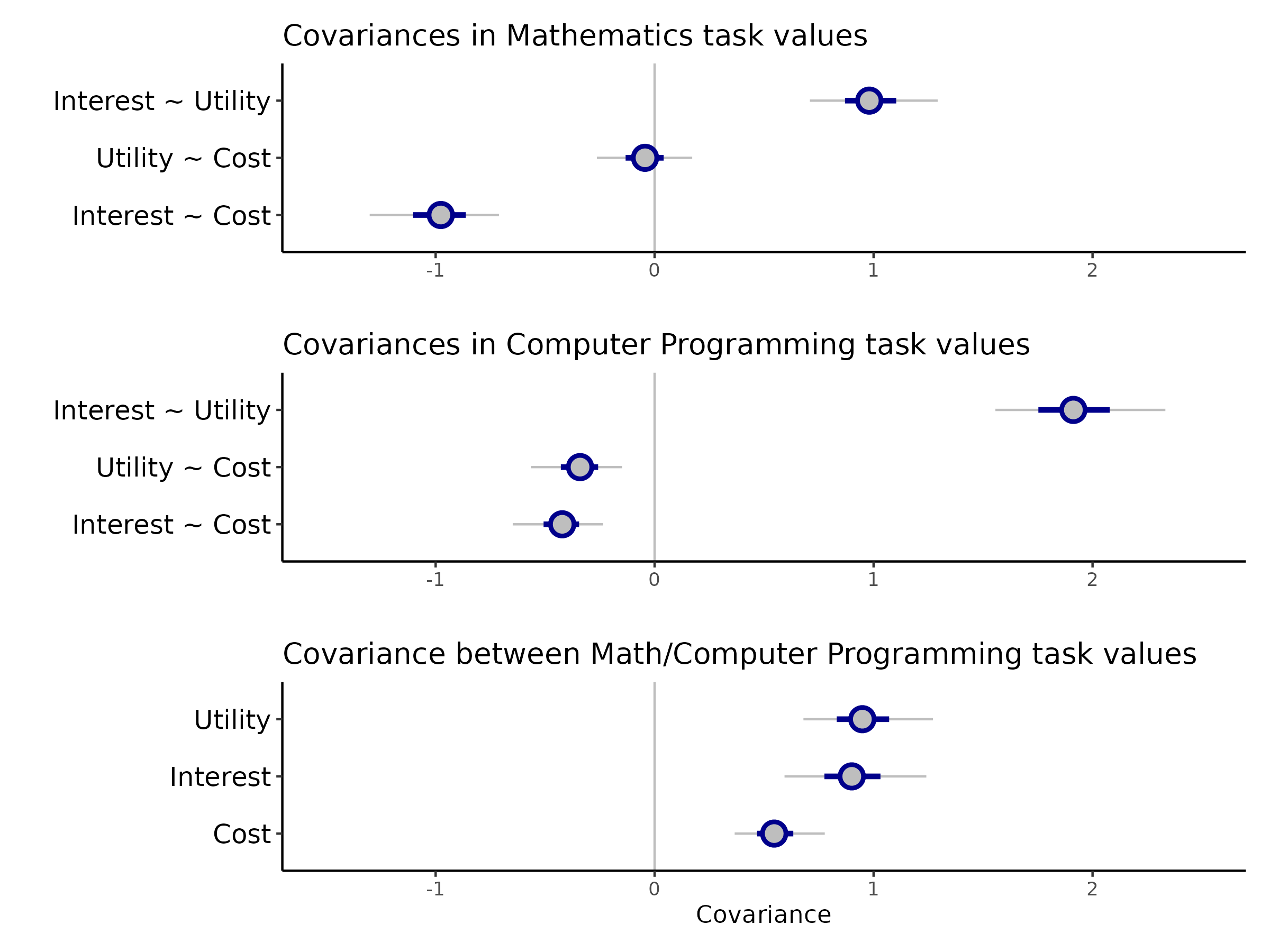
Do students have “suites” of attitudes towards mathematics and computer programming?
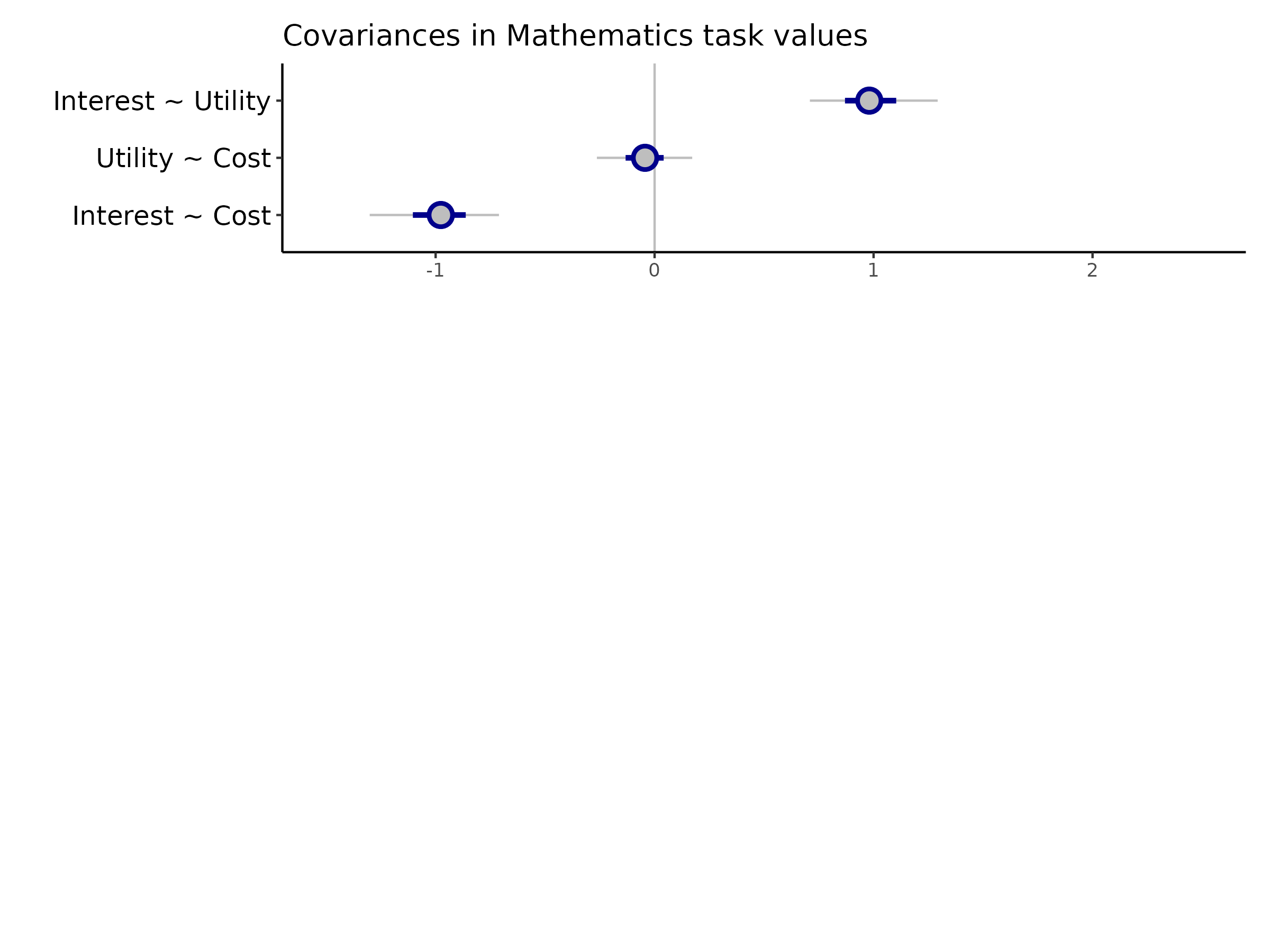
Approach: Interrogate covariance in students’ factor scores across task values
Do students have “suites” of attitudes towards mathematics and computer programming?
Do students have “suites” of attitudes towards mathematics and computer programming?
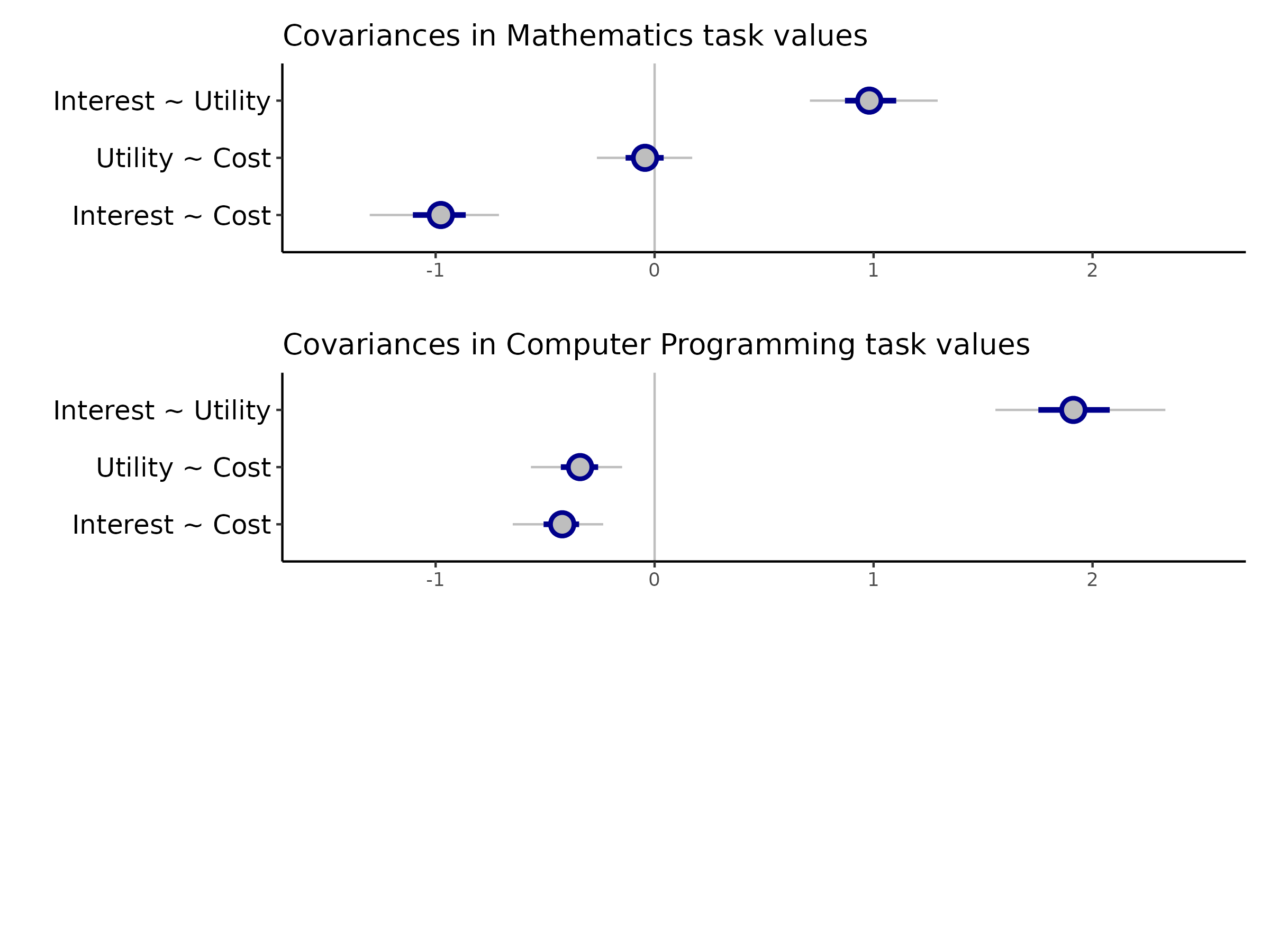
Do students have “suites” of attitudes towards mathematics and computer programming?
Do demographics explain student attitudes?
Short answer: We see no evidence for this.

Do demographics explain student attitudes?
Short answer: We see no evidence for this.
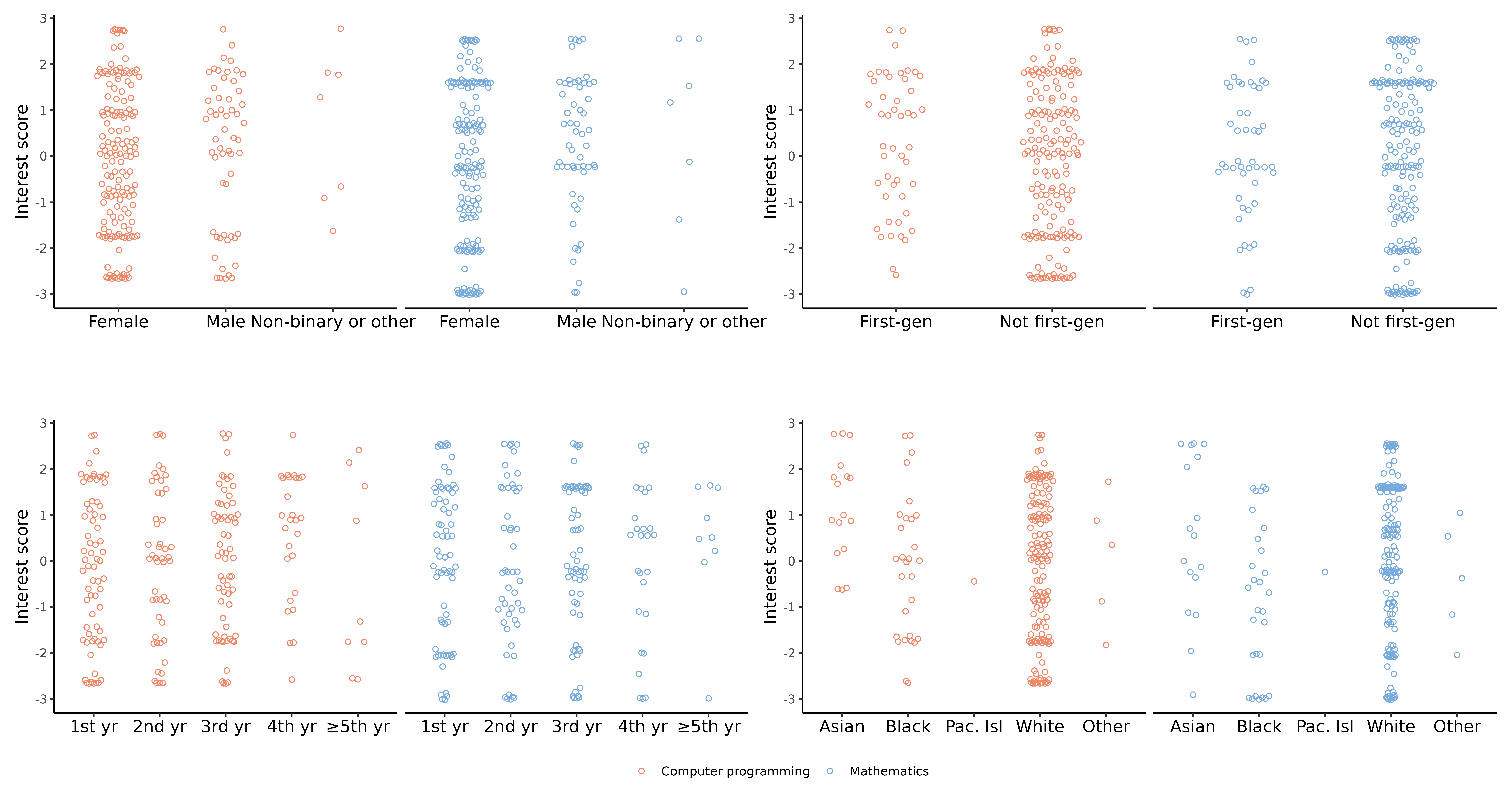
Results summary
Biology students perceive high utility of mathematics but low utility of computer programming for their careers.
Students who express higher interest in QCB also tend to perceive higher utility and lower cost (and vice-versa)
Implications
Implications
How to nudge task values?
Highlight/demonstrate utility of computer programming early on in education.
Perceived cost of QCB could limit student enrollment – so, incorporating this content into general (rather than specialized) biology courses is likely very important.
Help expand our scope and learn about your own students!

Help expand our scope and learn about your own students!

Questions we hope to address:
Do attitudes vary across institutions/types of institutions?
How are attitudes linked to student mindset?
Others you might be interested in!
Thanks for your attention.

Thanks for your attention.

Thanks also to LSU’s Vick Professorship for Educational Innovation, and to the faculty and students who have helped us conduct this survey.
We are conducting a parallel survey of scientist sentiments - we would love to hear from you.
References
Responses to all MBVI questions
Perceptions of interest quantified using student responses to four questions
(___ = mathematics or computer programming):
- Using [___] to understand biology intrigues/would intrigue me.
- It is/would be fun to use [___] to understand biology.
- Using [___] to understand biology appeals/would appeal to me.
- Using [___] to understand biology is/would be interesting to me.
Perceptions of utility quantified using student responses to four questions
(___ = mathematics or computer programming):
- [___] is valuable for me for my life science career
- It is important for me to be able to do [___] for my career in the life sciences.
- An understanding of [___] is essential for me for my life science career.
- [___] will be useful to me in my life science career
Perceptions of cost quantified using student responses to four questions
(___ = mathematics or computer programming):
- I have/would have to work harder for a biology course that incorporates [___] than for one that does not.
- I worry/would worry about getting worse grades in a biology course that incorporates [___] than one that does not.
- Taking a biology course that incorporates [___] intimidates/would intimidate me.
Responses to all MBVI questions

Convergence of Bayesian model fit
